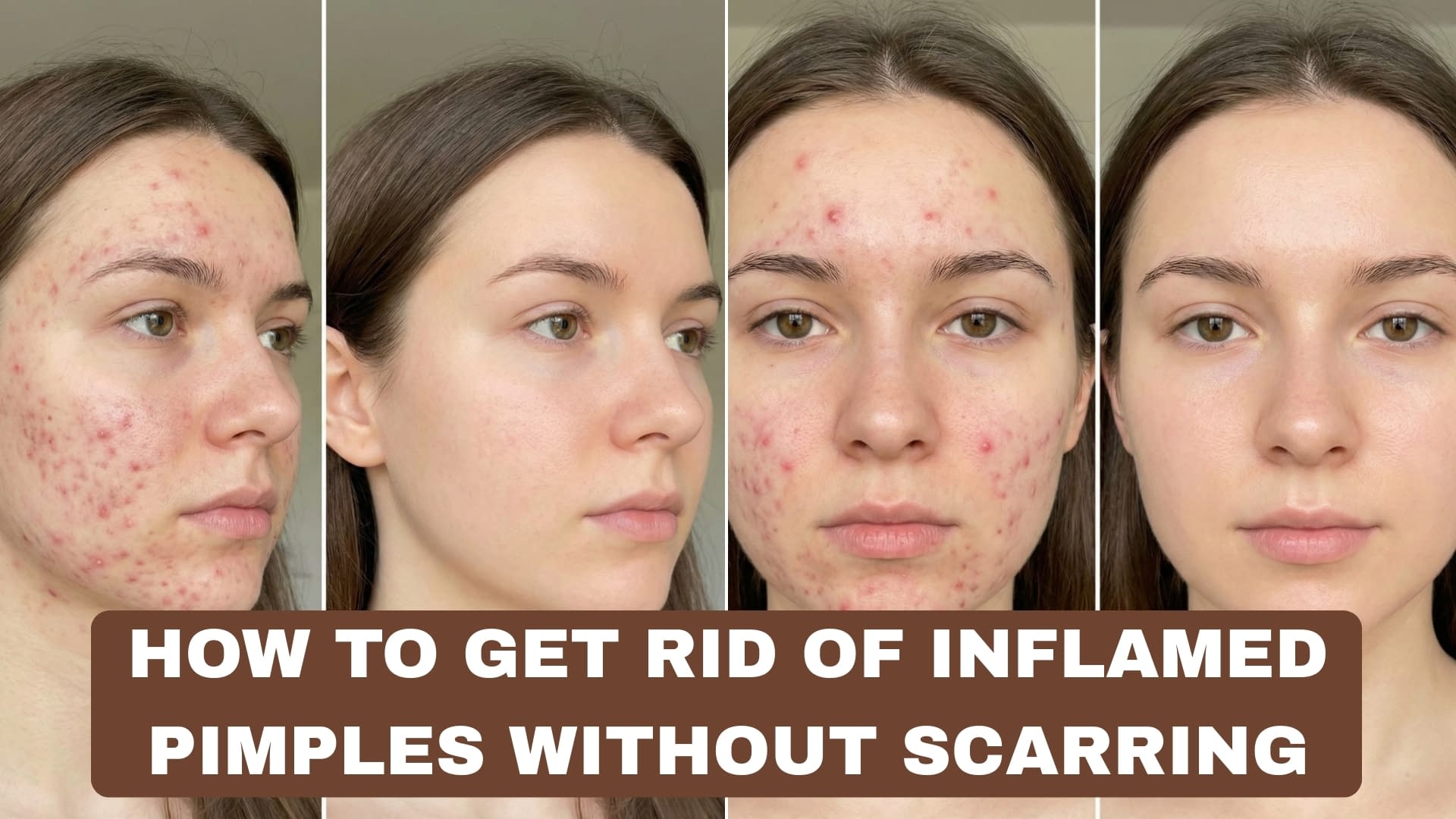
You want less shine without turning your face into a desert. Good — that’s sensible and doable. Oily skin is not a moral failing; it’s a mix of genetics, hormones, environment, and chores your skincare routine either helps or makes worse. This guide gives straight, practical steps (no nonsense, no miracle potions) to control oil, keep skin healthy, and avoid the classic mistake everyone makes: stripping the skin so hard it overcompensates by pumping out more oil.
Below you’ll find what causes oil, why aggressive drying backfires, plus detailed, step-by-step routines, ingredient guides, lifestyle advice, and makeup tips that actually work. Read it, pick the actions you’ll actually do, and follow them consistently. That’s where results live.
Understanding Oily Skin: Why Overproduction Happens
Short answer: your sebaceous glands are producing more sebum than necessary. Reasons vary — a few of the main causes:
- Genetics: some people are built with larger or more active sebaceous glands. Blame grandparents.
- Hormones: androgens (testosterone and relatives) ramp up oil production. That’s why teens and anyone with hormonal shifts see oil spikes.
- Skin barrier damage: when skin is stripped, it signals “we’re dry” and pumps out oil to compensate.
- Environment & climate: high heat and humidity = more sebum production.
- Lifestyle triggers: diet, stress, poor sleep, and certain medications can influence oil levels.
- Product misuse: heavy creams, occlusive oils, or comedogenic primers clog pores and make skin look greasier; harsh cleansers strip then rebound.
Realistic expectation: you can reduce visible oil, regulate production, and prevent clogged pores — but you can’t permanently change your genetics. You can, however, make your skin calmer and less greasy with better routine and product choices.
The Risks of Over-Drying: Why Stripping Oils Can Backfire
It looks logical: remove oil → less shine. But skin biology doesn’t care about logic, it reacts.
What happens when you over-dry:
- Rebound sebum production: skin senses dryness and increases oil to compensate.
- Compromised barrier: cracked, irritated skin loses moisture, becomes inflamed, and is more prone to acne and sensitivity.
- Increased sensitivity and redness: harsh alcohol toners and abrasive scrubs cause microtears and inflammation.
- Poor product performance: serums and actives penetrate unpredictably if the barrier is damaged.
How to avoid this trap (step-by-step):
- Stop overwashing: twice a day is enough for most people. If you exercise, rinse afterward.
- Drop harsh, alcohol-heavy toners and abrasive physical scrubs from daily use.
- Use gentle, targeted treatments (see sections below) rather than blasting skin with drying agents.
- Patch-test new actives to detect irritation early.
- Add a lightweight moisturizer even if you’re oily — this stabilizes the barrier and reduces rebound oil.
Takeaway: the goal is balance — control excess grease without shredding the skin’s defense.
Gentle Cleansing: Choosing the Right Cleanser for Your Skin Type

Cleansing controls surface oil, removes sunscreen/makeup, and preps skin for actives. Choose a cleanser that removes oil without causing irritation.
How to pick and use a cleanser (step-by-step):
- Choose the type:
- Gel or foaming cleansers — good for oily/combination skin; they remove excess sebum.
- Cream or micellar cleansers — better if your skin leans dry/sensitive but still oily (yes, combo skin exists).
- Low-pH, sulfate-free formulas minimize barrier disruption. Avoid cleansers with strong sulfates (SLS) if you have sensitive or reactive skin.
- Look for helpful ingredients:
- Salicylic acid (BHA, 0.5–2%) in a cleanser helps unclog pores (note: contact time is short with cleansers — leave-on is often more effective).
- Gentle surfactants and soothing additives like glycerin or niacinamide are a plus.
- Cleansing technique:
- Use lukewarm water (hot dilates dilates pores and irritates; cold isn’t efficient).
- Massage product with fingertips for 30–60 seconds focusing on T-zone.
- Rinse and pat dry — do not rub.
- Double cleanse at night if you wear makeup or sunscreen: oil-based first (dissolves sunscreen), then water-based to remove residue.
- Frequency: cleanse AM and PM; if you feel tightness, pick a gentler formula or cut back on other actives causing dryness.
Practical example routine:
- AM: gentle gel cleanser → toner (optional) → lightweight serum/moisturizer → SPF.
- PM: oil cleanser (if wearing sunscreen/makeup) → gel cleanser → targeted treatments → moisturizer.
Exfoliation Without Irritation: How to Keep Pores Clear Safely
Exfoliation sloughs dead skin and prevents clogged pores. But over-exfoliation creates inflammation and more oil. Balance and choice of exfoliant matter.
Types of exfoliants & when to use:
- Chemical exfoliants (preferred):
- BHAs (salicylic acid): oil-soluble, penetrates sebum and clears pores — ideal for oily skin and blackheads. Use leave-on serums or pads 2–4x/week depending on tolerance.
- AHAs (glycolic/lactic): water-soluble; excellent for surface texture and overall brightness. Use 1–3x/week or lower concentrations (5–10%) for regular use.
- Physical exfoliants: scrubs and brushes — use sparingly (once weekly max) and pick very gentle options. Avoid harsh apricot kernels, walnut shells, or aggressive brushes if you’re prone to breakouts.
- Enzyme exfoliants: (papaya, pineapple) — gentler, good for sensitive skin when used properly.
A safe exfoliation plan (step-by-step):
- Start slow: introduce one chemical exfoliant at a time and build frequency over 2–4 weeks.
- BHA routine: start with 1–2% salicylic acid leave-on product 2 nights a week. Increase to every other night if tolerated; many people use nightly but don’t rush.
- AHA spacing: alternate AHA nights with BHA or use AHA on separate nights (don’t stack strong AHA+BHA every night unless under supervision).
- One deep treatment weekly: a clay mask or wash-off AHA mask once a week can help absorb oil and refresh texture.
- Stop if irritated: redness, stinging, flaking beyond mild expected peel — stop, hydrate, and revert to gentler regime.
- Always apply SPF: chemical exfoliants increase sun sensitivity; sunscreen is non-negotiable.
Quick safety notes: avoid combining strong retinoids and aggressive acid routines without allowing skin to acclimate; that’s how you get sensitivity and the dreaded rebound oil.
Balancing Moisture: Lightweight Moisturizers That Won’t Make You Greasy

Yes, oily skin needs moisturizer. The right one prevents overproduction and locks in the benefits of your treatments.
What to look for in a moisturizer (step-by-step):
- Textures that work: gels, lightweight lotions, and water-based creams. Avoid very heavy creams or petroleum/jelly-based occlusives on the face unless nighttime and skin is dry.
- Ingredients to seek:
- Hyaluronic acid — hydrates without oil.
- Glycerin — humectant that draws water to skin.
- Niacinamide — reduces oil production and improves barrier function.
- Ceramides (in low concentrations) — restore barrier without greasiness.
- Non-comedogenic & oil-free — look for that labeling if you break out.
- Where to apply: a pea-sized amount for face; pat onto slightly damp skin to maximize hydration.
- Night vs day: use same light formula both AM and PM or a slightly more nourishing one at night if skin gets dry from actives.
Recommended layering order (simple):
- Cleanser → toner/serum (thinnest to thickest) → lightweight moisturizer → sunscreen (AM).
Pro tip: if you still feel greasy midday, prefer blotting papers over matte powders (which can mattify but build up and look cakey).
Targeted Treatments: Serums and Toners to Control Oil Production
Actives are your tools. Use them precisely and sparingly.
Key effective actives (what they do and how to use them):
- Niacinamide (2–5%) — reduces sebum production, improves barrier, calms redness. Safe day/night. Use alone or in combination with hyaluronic acid.
- Salicylic acid (BHA) — for pore clearing. Best as leave-on serum/pad; start 2–3x/week.
- Azelaic acid (10–15%) — reduces inflammation, clears pores, evens tone. Good for sensitive/acne-prone oily skin. Use 1–2x day.
- Retinoids (retinol, tretinoin, retinaldehyde) — improve cell turnover, reduce comedones, smooth texture; use gradually at night 2–3x/week building up. Not for pregnancy.
- Zinc PCA or topical zinc — reduces oil and has mild sebum-regulating properties.
- Clay masks (kaolin, bentonite) — weekly oil absorption and pore unclogging treatment.
How to build a practical targeted regimen (step-by-step):
- Start with the basics: niacinamide AM, BHA 2–3 nights/week PM (alternate).
- Introduce retinoid slowly: start 1–2 nights/week, increase frequency gradually. If using retinoid, use BHA on separate nights to lower irritation risk.
- Add azelaic acid if you need extra anti-inflammatory action or if you’re sensitive to retinoids.
- Weekly clay mask: use once weekly after cleansing to control surface oil. Rinse after it dries to the point of almost dry (don’t let it crack heavily).
- Be patient: actives take weeks to months to change baseline oil production and pore clarity.
Caution: mixing certain actives (high-strength AHA + high-strength retinoid + BHA) increases irritation risk; layer thoughtfully.
Diet and Lifestyle Tips to Help Reduce Excess Oil Naturally

You won’t fix everything with food, but diet & habits influence sebum and inflammation.
Practical diet & lifestyle steps (step-by-step):
- Hydrate consistently: water helps skin balance. Don’t expect miracles, but dehydration can worsen texture and oil management.
- Cut extreme refined sugar and high-GI foods: spikes in insulin can increase sebum production indirectly. Swap sugary snacks for protein/fiber snacks.
- Include healthy fats: omega-3s (fatty fish, flaxseed, walnuts) reduce inflammation and may help skin health.
- Limit dairy if you suspect it’s a trigger: some people see breakouts/oil spikes with high dairy intake — try a 2–3 week elimination if you suspect a link.
- Manage stress and sleep: poor sleep and high stress upregulate cortisol, which can affect sebum production. Aim for regular sleep and short stress-reduction practices.
- Exercise & sweat: exercise improves circulation and skin turnover; cleanse after sweating.
- Avoid smoking & limit alcohol: both worsen inflammation and barrier health.
Keep a simple food & skin log for two weeks if you suspect diet is affecting oil; patterns often reveal themselves.
Sun Protection for Oily Skin: How to Avoid Breakouts While Staying Safe
Sunscreen is mandatory for skin health and for safe use of many actives — the trick is to pick one that won’t add grease.
How to choose & apply sunscreen (step-by-step):
- Pick non-comedogenic, oil-free formulas: gel or fluid textures are best for oily skin.
- Mineral (zinc/titanium) vs chemical: modern mineral formulas can be lightweight; chemical sunscreens can be light too. Try samples to see what works with your skin and makeup.
- Tinted sunscreens often double as light coverage and reduce the need for heavy foundation (less product = less grease).
- Apply enough: use about a nickel-sized amount for the face; pat on rather than rub to avoid moving product layers.
- Reapply every 2 hours when outdoors; blot with paper and reapply thinly if you’re oily — or use SPF powders for quick midday touch-ups.
- Look for added benefits: some sunscreens include niacinamide or antioxidants, which help oily/blemish-prone skin.
Sunscreen myth: “It will make me greasy.” Not if you pick the right formulation.
Makeup Tips for Oily Skin: Products That Control Shine Without Dryness

Makeup should disguise oil, not make you feel like you’re wearing armor. Use lightweight, breathable products and smart techniques.
Makeup routine & product picks (step-by-step):
- Primer: use a silicone-based primer only where you need smoothing/blur (T-zone). Don’t prime the whole face if it makes you mask-like.
- Foundation: pick thin, buildable, oil-free or water-based foundations. Tinted moisturizers or lightweight serum foundations are great for everyday.
- Concealer: use sparingly only on spots and under eyes. Avoid heavy layers under eyes if they crease.
- Set wisely: press a minimal amount of translucent powder onto the T-zone with a damp sponge to avoid cakiness. A light dusting with a fluffy brush will overdo it.
- Blotting papers: carry them and press (don’t rub) to remove midday shine. Reapply powder only if necessary.
- Matte vs luminous: if you prefer a glow, use cream-based highlighters on cheekbones only — keep the T-zone matte.
- Oil-control setting sprays: a light mist after makeup can reduce immediate shine but test to make sure it doesn’t break you out.
- Brush hygiene: clean tools weekly; oil and bacteria build-up on brushes increase shine and breakouts.
Makeup trap to avoid: heavy layers to “cover” oil — they look cakey and trap oil underneath.
Daily Habits That Keep Your Skin Fresh and Balanced All Day
The small daily choices add up. These habits keep oil under control and prevent bad rebounds.
Daily habit checklist (step-by-step):
- AM: gentle cleanse → niacinamide serum → lightweight moisturizer → SPF.
- PM: double cleanse if wearing sunscreen/makeup → targeted treatment (BHA/retinoid/azelaic according to your schedule) → moisturizer.
- Weekly: clay mask once a week; gentle physical exfoliation once weekly if desired; laundry pillowcase weekly to avoid oil transfer.
- Midday: blotting papers and a light dusting of powder if needed; avoid washing face excessively (that causes rebound).
- Hands-off: don’t touch your face all day; fingers transfer oil and bacteria.
- Keep hair clean: oily hair that touches the face transfers oil. Tie it back if needed.
- Switch products thoughtfully: change one thing at a time and give it 4–8 weeks.
- Track and tweak: take photos every 2–4 weeks to track progress; skin changes slowly.
Sustainability: pick products you’ll use consistently. The best product is the one you actually apply.
Final Words
Oily skin responds to consistency, not drama. The simple truth: stop stripping the skin, choose targeted actives (BHA, niacinamide, retinoids as needed), hydrate with lightweight moisturizers, protect with non-comedogenic sunscreen, and use sensible makeup tactics. Lifestyle choices — sleep, stress control, and a balanced diet — back up everything you do topically.
Start with a realistic, two-week trial: adopt a gentle cleanser, add niacinamide AM and a BHA product PM (on alternating nights), hydrate with a lightweight moisturizer, and use SPF every morning. Give the routine 6–12 weeks for real change. If you’re still drowning in oil after well-executed basics, see a dermatologist — there are prescription options and in-office treatments that can help.
Do the steady, boring things well. That’s how you get less shine and healthier skin — without wrecking your face.Think